Ketogenic amino acids are an amino acid that can be degraded straightforwardly into acetyl-CoA, which is the forerunner of ketone bodies and “myelin, particularly during early turn of events when mind myelin amalgamation is very high,” as per the National organization of Health.
This is as opposed to the glucogenic amino acids, which are changed over into glucose. Ketogenic amino acids can’t be changed over to glucose as both carbon iotas in the ketone body are at last degraded to carbon dioxide in the citrus extract cycle.
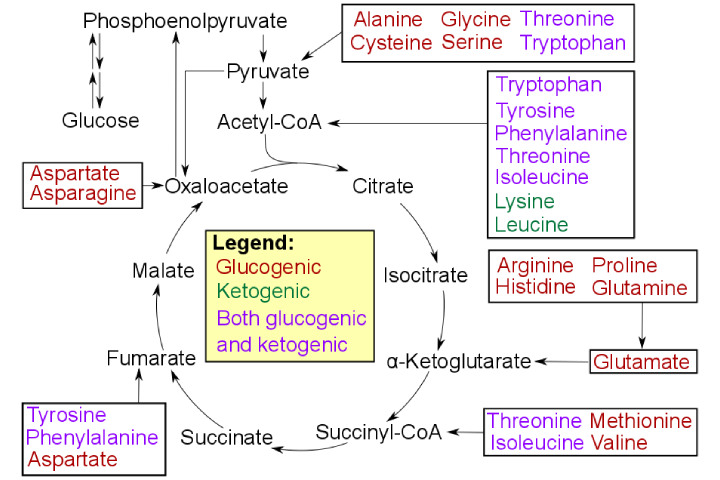
In humans, two amino acids – leucine and lysine – are solely ketogenic. Five more are both ketogenic and glucogenic: phenylalanine, isoleucine, threonine, tryptophan, and tyrosine. The remaining thirteen are solely glucogenic.
Source: Wikipedia
Table of Contents
1. Types of Amino Acids
amino acids can be categorized into two types depending upon their catabolic pathways
Glucogenic Amino Acids
The carbon skeletons are changed over into pyruvate, 2-oxoglutarate, succinyl-CoA, fumarate, and oxaloacetate, and they go about as glucose forerunners.
Ketogenic Amino Acids
The carbon skeletons are catabolized to acetyl-CoA or acetoacetate and can, in this manner, lead to the creation of unsaturated fats or ketone bodies.
2. Their Roles in Your Body
Essential amino acids perform fluctuated functions in your body. They’re associated with significant cycles, for example, tissue development, vitality creation, insusceptible capacity, and supplement assimilation.
What Makes an Amino Acid Ketogenic?
A ketogenic amino acid is an amino acid that can be debased legitimately into acetyl-CoA, which is the forerunner of ketone bodies and “myelin, particularly during early turn of events when cerebrum myelin combination is very high,” as indicated by the National organization of Health.
3. Characteristics of Amino Acids
Amino Acids Are Basic Units of Protein
- All amino acids have, in any event, one acidic carboxylic acid (- COOH) gathering and one essential amino (- NH2) gathering.
- Amino acids are bland, glasslike strong.
- They are dissolvable in water and insoluble in natural dissolvable.
- Just L-type amino acids are found in protein in the human body. If D-structure is available, it is changed over into l-structure by proteins in the liver.
- More than 300 amino acids are found in nature; however, just 20 amino acids are standard and present in protein since they are coded by quality.
- Other non-standard amino acids are changed amino acids and called non-protein amino acids.
4. Some examples of Modified amino acids
- 4-hydroxyproline: synthesized from proline
- 5-hydroxylysine: synthesized from lysine
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA): synthesized from glutamic acid
- Gamm-Carboxylglutamate: synthesized from glutamic acid
- Desmosine: synthesized from lysine
5. Classification of Amino Acids
- Classification based on R-gathering
- Classification based on nourishment
- Classification based on Catabolism
a. Classification of Amino Acids Based on R-gathering
Nonpolar, Aliphatic amino acids: The R bunches in this class of amino acids are nonpolar and hydrophobic—glycine, Alanine, Valine, leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, Proline.
Sweet-smelling amino acids: Phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan, with their sweet-smelling side chains, are moderately nonpolar (hydrophobic). All can partake in hydrophobic communications.
Polar, Uncharged amino acids:
The R gatherings of these amino acids are more solvent in water or more hydrophilic than those of the nonpolar amino acids. They contain useful assemblages that structure hydrogen bonds with water. This class of amino acids incorporates serine, threonine, cysteine, asparagine, and glutamine.
Acidic amino acids: Amino acids in which R-bunch is acidic or contrarily charged. Glutamic acid and Aspartic acid
Essential amino acids: Amino acids in which R-bunch is critical or emphatically charged. Lysine, Arginine, Histidine
b. Classification of Amino Acids Based on nutrition
Essential Amino Acids (Nine)
Nine amino acids can’t be orchestrated in the body and, like this, must be available in the eating regimen all together for protein combination to happen.
These essential amino acids are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine.
Trivial Amino Acids (Eleven)
- These amino acids can be orchestrated in the body itself and thus should not be procured through eating routine.
- Arginine, glutamine, tyrosine, cysteine, glycine, proline, serine, ornithine, alanine, asparagine, and aspartate.
- Conditionally
Classification of Amino Acids Based on the Metabolic Destiny
Glucogenic amino acids: These amino acids fill in as forerunners gluconeogenesis for glucose Classification. Glycine, alanine, serine, aspartic acid, asparagine, glutamic acid, glutamine, proline, valine, methionine, cysteine, histidine, and arginine.
Ketogenic amino acids: this amino acid breakdown to shape ketone bodies. Leucine and Lysine.
Both glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids: These amino acids breakdown to shape antecedents for ketone bodies and glucose. Isoleucine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, and tyrosine.
6. Regulation of Amino Acid Metabolism and Liver Disease
Hepatic amino acid digestion is mostly controlled by substrate flexibly in the present moment. Amino acids take-up by hepatocytes rely upon dietary amino acids’ appearance to the liver in the fed state and on the net pace of body protein breakdown in the starved state, which is under hormonal control.
On long haul premise, amino acid digestion is controlled by the hormones glucagon and cortisol, just as by amino acids gracefully. Glucagon initiates amino acid carriers, especially for alanine, to build amino acid take-up.
The measure of dietary protein has a drawn-out control of hepatic catalysts of amino acid digestion. When the dietary protein content is low, these catalysts are smothered, while the declaration of these chemicals is animated when dietary protein is more than sufficient.
Along these lines, the liver controls the store of amino acids. In patients with liver illness, protein digestion guidelines are regularly upset and changed with ailment etiology and seriousness.
In liver malady, the adjusted protein and amino acid digestion is related with diminished degrees of circling extended chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) and raised degrees of flowing aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tryptophan, and tyrosine) with attendant changes in amino acid energy (Blonde-Cynober et al., 1999).
There is expanded endogenous leucine motion in patients with cirrhosis, a pointer of protein breakdown, and diminished protein blend in light of a feast. These progressions will bring about clinically apparent muscle squandering, showing as protein-calorie unhealthiness and low degrees of liver combined plasma proteins.
7. Health Advantages of Supplementing With Essential Amino Acids
Increase Muscle Growth
The Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) assume a significant part in building muscle. In any case, your muscles require all the essential amino acids for the best outcomes.
Lessening Muscle Soreness
Enhancing with BCAAs may diminish muscle irritation by lessening harm in practiced muscles.
Decrease Exercise Fatigue
BCAAs might help diminish activity instigated exhaustion. However, they are probably not going to improve practice execution.

Reduce Muscle Wasting
Taking BCAA enhancements can forestall the breakdown of protein in specific populaces with muscle squandering.
Prevent People With Liver Disease
BCAA enhancements may improve individuals with liver illness’s well-being results while additionally perhaps securing against liver malignancy.