The saphenous nerve (long or inward saphenous nerve) is the most significant cutaneous part of the femoral nerve. It is a carefully tactile nerve and has no motor work.
This nerve is the continuation of the femoral nerve. It is an unadulterated tangible nerve that dives into the quadriceps muscle in the Subsartorial waterway. The nerve arises from the channel by puncturing a fascial layer 10 cm over the knee, emitting branches for the knee’s skin.
It dives down the average side of the tibia. The saphenous nerve innervates the middle part of the lower leg’s skin, the lower leg (the average malleolus), and a little bit of the curve of the foot, near the saphenous vein.
Table of Contents
1. What is the Function of the Saphenous Nerve?
The saphenous nerve is a tactile part of the femoral nerve (lumbar plexus L3, L4) and supplies sensation to the anteromedial, average, and posteromedial surface of the leg. The saphenous nerve is the most significant terminal cutaneous part of the femoral nerve (dorsal divisions of the ventral rami of L2-L4).
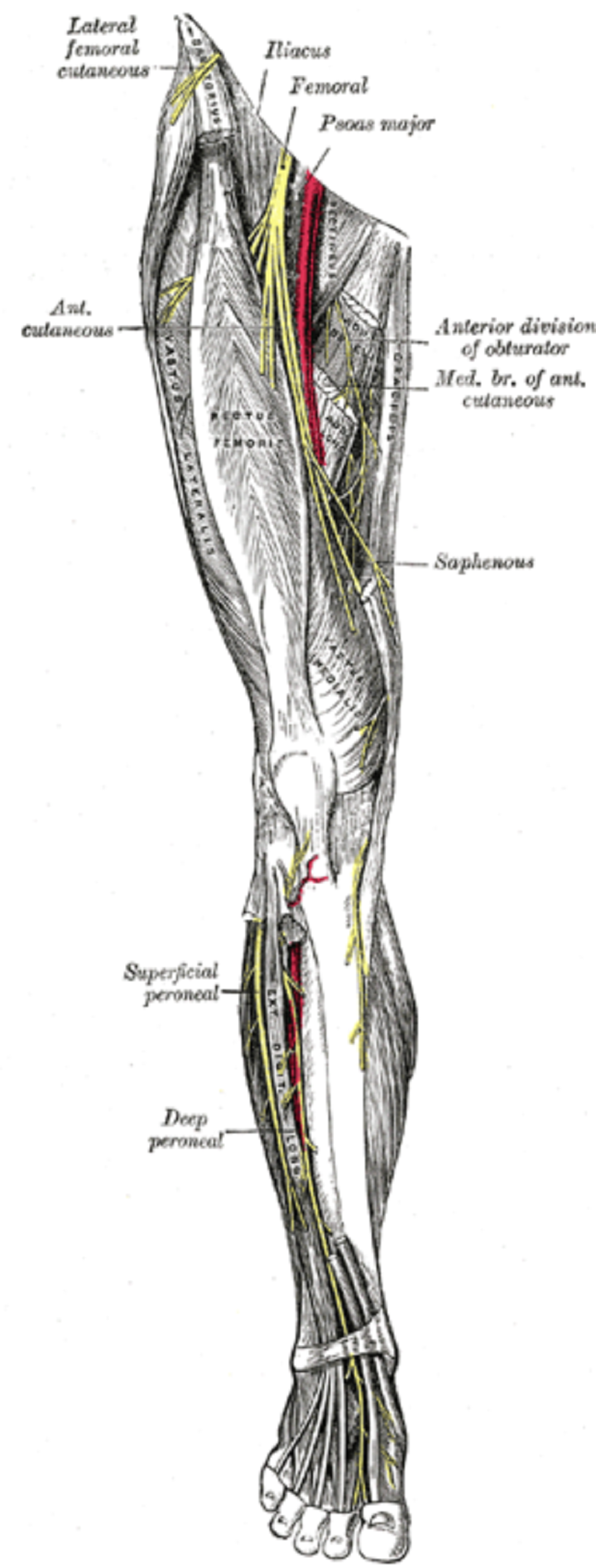
source: Wikipedia
2. How Would You Test for the Saphenous Nerve?
An agony incitement test can be utilized to decide the presence of neuropathy of the saphenous nerve. The patient is an afterthought, the hip is expanded and abducted, and the knee flexed. Imaging of the saphenous nerve in MRI is frequently troublesome since the nerve has a level morphology.
3. Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of saphenous nerve ensnarement may incorporate a profound thigh hurt, knee agony, and paresthesias in the nerve’s cutaneous appropriation in the leg and foot. The infrapatellar branch may become entangled alone because it goes through a different foramen in the sartorius ligament.
It might likewise be presented to injury where it runs evenly over the noticeable quality of the average femoral epicondyle. Patients report paresthesias and deadness in the infrapatellar district that exacerbates knee flexion or pressure by clothing or support articles.
Saphenous nerve entanglement is a now and again neglected reason for constant average knee torment in patients who experience injury or hard impacts on the knee’s middle part. Since the saphenous nerve is tactile, a separated physical issue to this nerve should not bring about the shortcoming.
4. Saphenous Nerve Damage: Signs
This nerve is regularly harmed during vein collect for CABG since it runs with the saphenous vein, or by trochanter arrangement during knee arthroscopy.
- The indication of saphenous nerve damage is the loss of sensation over the lower leg’s middle part.
- The nerve can be obstructed simply over the average malleolus, at the degree of the tibial tuberosity, or utilizing a transarterial approach.
5. What is it Block Utilized for?
- For wound fix or investigation of the lower leg or lower leg
- As a significant aspect of a lower leg block needed to control a cracked or disengaged lower leg
- For entry point and seepage of a sore in the lower leg or lower leg
- For unfamiliar body evacuation in the lower leg or lower leg
- To control torment after careful fix of the meniscus.
6. What Are the Risks and Complications of a Saphenous Nerve Block?
Confusions of a saphenous nerve block method include:
Contamination: Any strategy that includes infusing drugs into the skin can cause disease. This can happen if the infusion site isn’t appropriately cleaned preceding the technique.
Nerve injury: If the sedative medicine is infused into the nerve itself, it might bring about brief or perpetual harm to the nerve. The patient may have deadness, shivering, or agony at the infusion site if this happens.
Unfavorably susceptible response: Most sedative squares are protected and infrequently cause hypersensitive reactions. When unfavorably susceptible responses happen, they can run from deferred excessive touchiness (gentle tingling and expanding) to full anaphylactic stun.
On the off chance that you have a known hypersensitivity to injectable sedative meds, for example, lidocaine or bupivacaine, examine this with your primary care physician preceding getting a saphenous nerve block.
Dying: Because a saphenous nerve block is performed with an injectable prescription, seeping under the skin (wound or hematoma) may happen.
7. Surgical Anatomy of the Saphenous Nerve
The front leg compartment’s surface life systems have concentrated on the saphenous vein(SV), ignoring the saphenous nerve (SN). The SV is frequently utilized as a join during vascular detour procedures. During the SV’s harvest, the specialist must focus on the most important relationship with the SN. Visit this website to find the right specialist who can help carry forward the procedure.
An indiscreet analysis or absence of information on this nerve’s life structures or branches will lead to sensory adjustments (torment, paresthesias, and sedation) in the middle part of the leg. Saphenous neuralgia depicts the indication com-plex that incorporates sedation, hyperesthesia, and pain within the SN’s circulation.
Other than its description after SV gathering for coronary vein sidestep graft procedures, it has additionally been depicted after varicose vein, arterial, and orthopedic procedures.
We focused our consideration on the SN in the leg, as it is in this locale wherein associations with the SV matter and where the SN is at its most danger of being harmed.
8. Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
This nerve block’s execution requires an interprofessional coordinated effort between the proceduralist, nursing staff, and clinical drug specialist. The patient should be on ceaseless hemodynamic observing, and crisis aviation route hardware, supplemental oxygen, and revival drugs (counting lipid emulsion) kept promptly accessible.
Colleagues should know the early indications of nearby sedative fundamental poisonousness (i.e., tinnitus, circumoral deadness, and metallic taste) and alert patients encouraged to report them. First, acknowledgment and treatment are essential to staying away from more severe complexities, including seizures and cardiovascular breakdown.
Suppliers should compute the most extreme weight-based portion of the neighborhood before the beginning of the strategy and should utilize the least successful dosing to limit the danger of fundamental poisonousness; this should remember the clinician drug specialist for a shared exertion.
Nursing will aid the methodology and give easy checking, illuminating the clinician regarding any worries that may emerge. With an interprofessional way to deal with the nerve block, results will be improved.

